
Therefore, the aim of our study was to report the incidence of incidental cartilage injuries and their management in arthroscopic treatment of MFC. However, the optimal treatment is still not clear and there is limited data on concomitant injuries of cartilage. This is controversial and can be discussed with your surgeon.The Maisonneuve fracture complex (MFC) is a well-known lower leg injury. Additionally, some surgeons recommend a second surgery to remove the hardware used to repair the syndesmosis before returning to weight bearing. Most surgeons will immobilize the ankle for 4-6 weeks after surgery and prevent weight-bearing of the limb for 6-12 weeks after surgery. Rehabilitation after a Maisonneuve fracture can take several months, depending on the severity of the injury and the surgeon’s guidelines. A few centimeters above the ankle joint, the joint is repaired with screws or very heavy suture material. The key structure that needs to be kept in place is the syndesmosis (the ligament that connects the tibia). However, fibula fractures around the knee do not require surgical fixation. When repairing a Maisonneuve ankle fracture, the medial side (medial) is repaired, the syndesmosis is repaired. However, the typical treatment for Maisonneuve fractures is surgery to restore stability to the ankle. Surgery is the standard of care for Maisonneuve fractures, but nonsurgical treatment may be considered in some patients with nondisplaced fractures or ankles, or in patients who do not respond well to surgery (elderly or ill). READ ALSO: Prevent hip replacement dislocation Instability becomes apparent when forces are placed on the ankle joint. To make a diagnosis, your healthcare provider may need to get special X-rays that put pressure on the ankle joint. A normal x-ray of the ankle joint may not clearly show this ligament injury. This ligament injury can lead to ankle instability that requires treatment. This injury is difficult to detect as there are often minor fractures below the knee joint, but there is significant damage to the ligaments all the way to the ankle. The energy of the injury travels through the ankle ligaments adjacent to the leg bone (the syndesmotic ligament) and through the fibula. When this injury is forceful, it overcomes the strength of the bones and ligaments. Most of the time, the foot hits the ground and the extremity rotates inward, causing compression of the bones and ligaments. Maisonneuve fractures occur as a result of rotational injuries to the ankle joint.

#Maisonneuve fracture skin#
The skin should be examined for signs of fractures, blisters and other severe soft tissue damage. In some patients, there is severe soft tissue damage that can complicate treatment. The patient will have an X-ray to determine the pattern of damage, and a knee X-ray if there is concern that the injury is a Maisonneuve fracture.
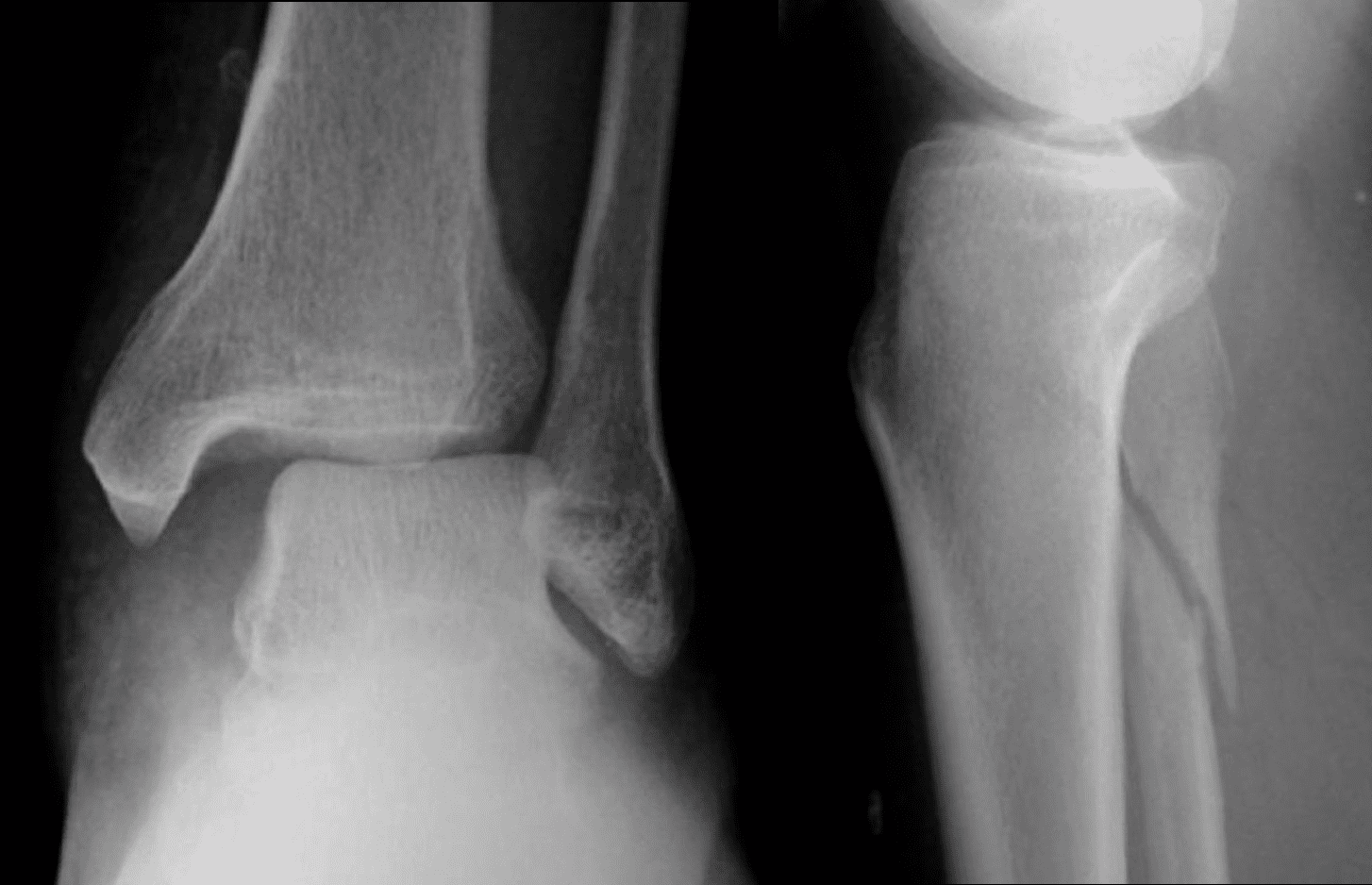
Fractures are important because treatment almost always requires surgery, and without careful examination of the ankle (and knee), there is a risk of misdiagnosing the injury. A Maisonneuve fracture is a specific type of ankle fracture that occurs when the ankle is twisted outward with force (external rotation).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
